Beginner
Understanding Neutral Posture
Neutral posture represents the natural alignment of your body when you're completely relaxed.
Learn to identify and maintain this position to minimize strain on muscles, joints, and ligaments.
This foundational concept applies whether you're sitting, standing, or moving between positions.
Key elements include maintaining the natural curves of your spine, keeping joints at their
resting angles, and positioning your body so muscles can work efficiently without unnecessary
tension or compression.

Beginner
Pelvic Positioning for Comfort
Your pelvis serves as the foundation for spinal alignment. When positioned correctly, it
allows your spine to maintain its natural S-curve, reducing pressure on intervertebral discs
and preventing compensatory postures elsewhere in your body.
Focus on sitting on your sit bones rather than your tailbone, and avoid excessive anterior
or posterior pelvic tilt. This creates the optimal base for comfortable, sustainable sitting.
Beginner
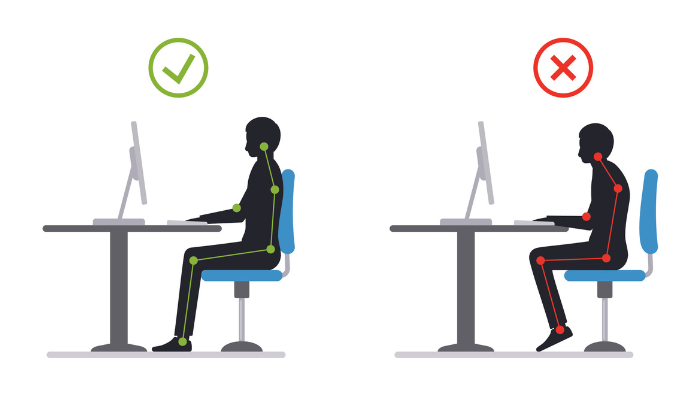
Correct vs Incorrect Posture
Visual comparison of proper ergonomic alignment versus common postural faults. Understanding
the difference between healthy and harmful positions helps you recognize and correct problematic
habits before they lead to discomfort or injury.
Notice how correct posture maintains spinal curves, keeps shoulders relaxed, and positions
the head directly above the shoulders. Poor posture shows the characteristic forward head
position and rounded shoulders that contribute to neck and upper back pain.
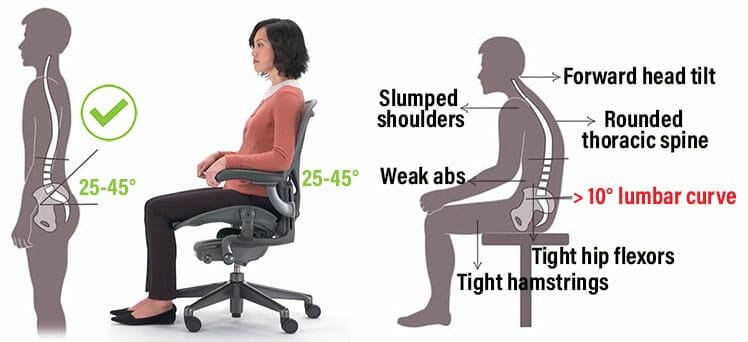
Advanced
Spinal Alignment Deep Dive
Detailed analysis of how proper spinal alignment affects your overall health and productivity.
Learn about the three natural curves of your spine and how maintaining them reduces muscle
fatigue, improves circulation, and enhances cognitive function.
Explore the relationship between lumbar support, thoracic extension, and cervical positioning.
Understand how each segment of your spine contributes to overall postural health and what
happens when these natural curves are compromised.

Quick Fix
Quick Posture Check (2 Minutes)
A rapid assessment you can perform multiple times daily to ensure your body remains in
optimal alignment. This simple check helps you catch postural drift before it becomes
problematic and reminds you to reset your position.
Focus on five key alignment points: feet flat on the floor, sit bones properly positioned,
spine maintaining natural curves, shoulders relaxed down and back, and head centered over
shoulders. Spend 30 seconds on each point.

Beginner
Break Schedule Fundamentals
Regular breaks prevent muscle fatigue, maintain circulation, and refresh mental focus.
The 20-20-20 rule suggests taking a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something
20 feet away, giving your eyes and postural muscles a rest.
Implement micro-breaks of 30 seconds every 30 minutes for posture resets, and longer
movement breaks every 2 hours to stand, stretch, and walk. These intervals are based on
research into optimal recovery periods for sustained desk work.

Advanced
Micro-Movement Strategies
Small, frequent movements throughout your workday prevent stiffness and maintain muscle
engagement. These subtle adjustments don't disrupt productivity but provide continuous
circulation and postural variety that keeps your body healthy.
Learn to shift weight periodically, perform subtle spinal movements, adjust arm positions,
and change foot positions. These micro-movements activate different muscle groups and
prevent the static positioning that leads to discomfort.

Beginner
Dynamic vs Static Positioning
Understanding why varying your position throughout the day improves comfort and health.
Dynamic sitting involves subtle movements within your seated position, while static
postures maintained for extended periods increase strain on specific muscle groups.
Learn to incorporate gentle swaying, occasional position shifts, and micro-adjustments
that keep muscles active without requiring you to stand or leave your workspace. This
approach maintains engagement while allowing natural movement.

Quick Fix
Environment Cues for Posture
Use your physical environment as visual and tactile reminders to maintain proper posture.
Strategic placement of objects, lighting adjustments, and workspace modifications can help
you maintain awareness of your positioning throughout the day.
Position mirrors to see your side profile, use monitor placement as a cue for head position,
and create visual markers for optimal keyboard and mouse placement. These environmental
cues become automatic reminders that support postural awareness.








