
Beginner
Perfect Monitor Height & Distance
The top of your screen should be at or slightly below eye level, approximately 20-26 inches
from your face. This positioning allows for slight downward viewing (10-20 degrees) which
is more comfortable than looking straight ahead or up. The center of your screen should
align with your nose when facing forward.
If using multiple monitors, position your primary screen directly in front of you and
angle secondary screens toward your face. This reduces the need for neck rotation and
maintains more natural head positioning throughout your workday.
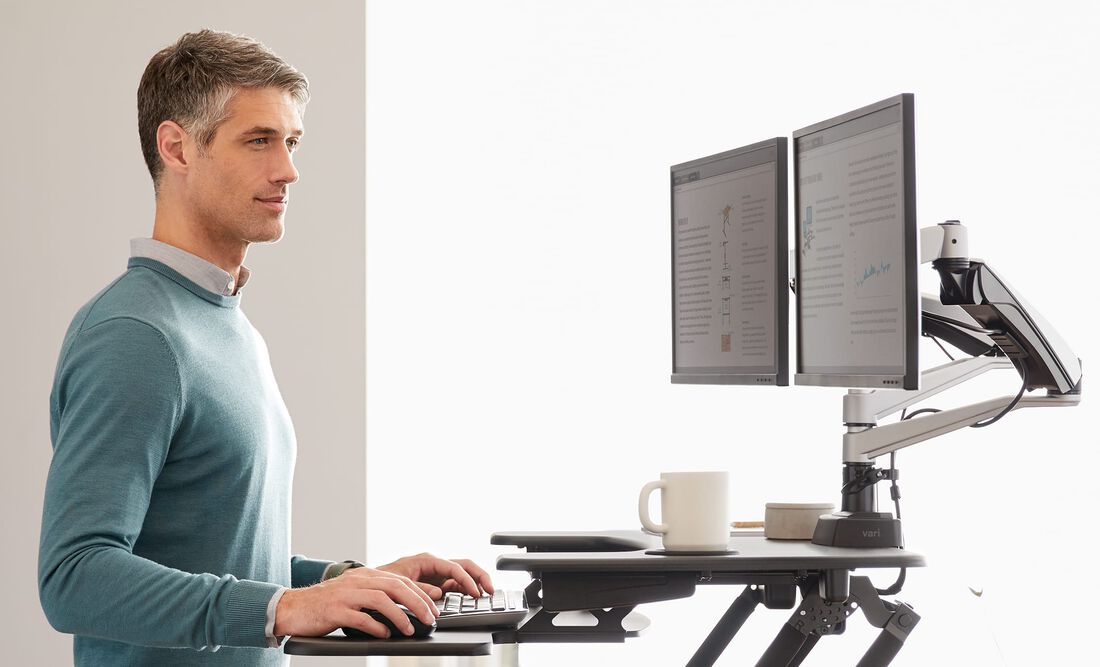

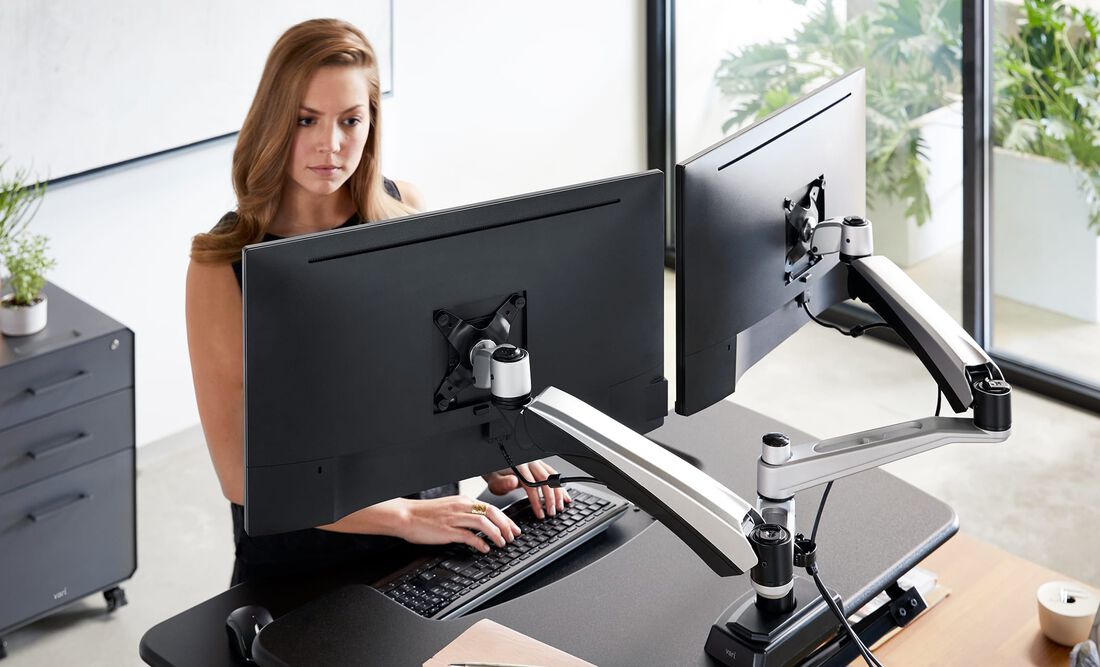
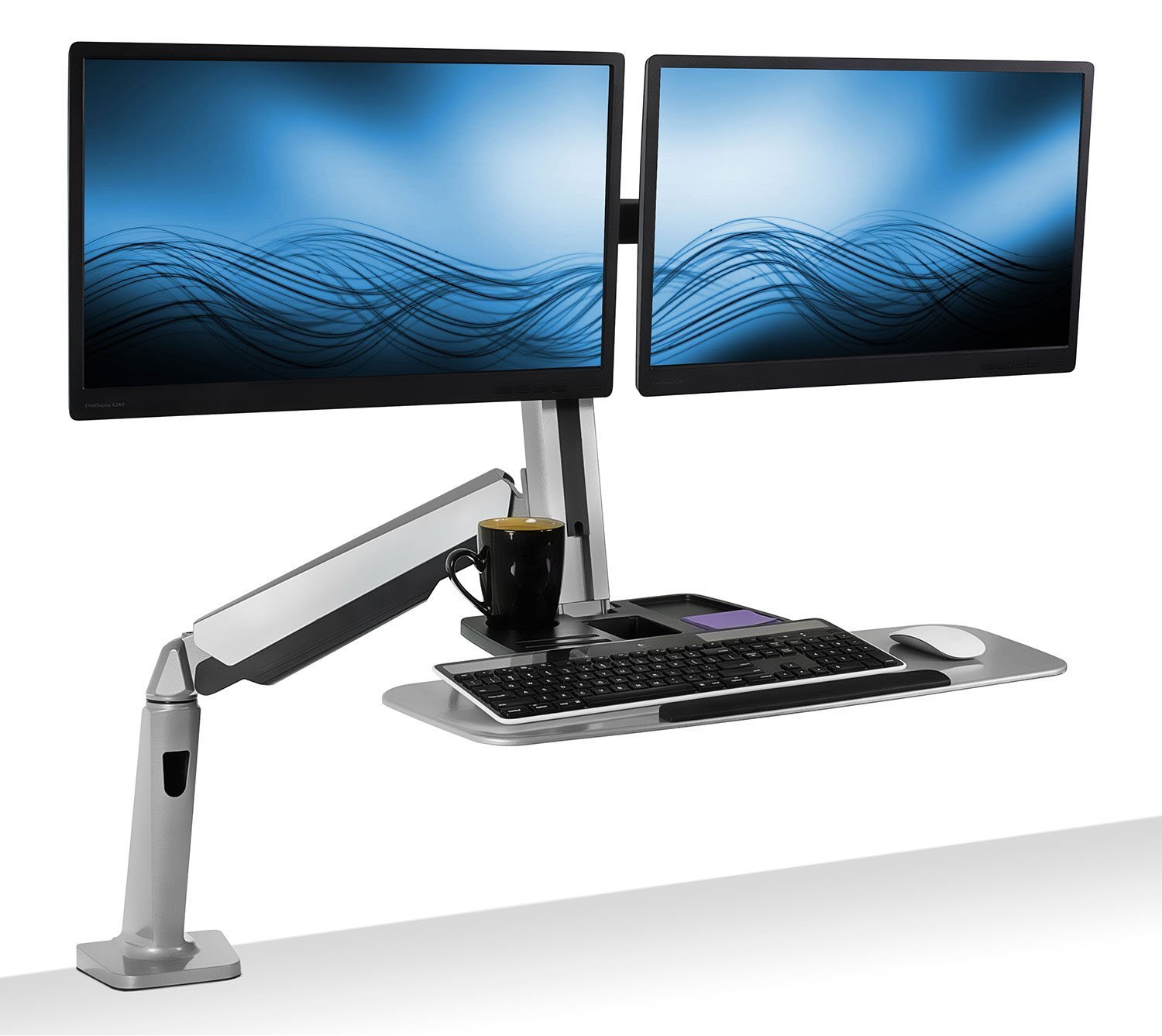
Advanced
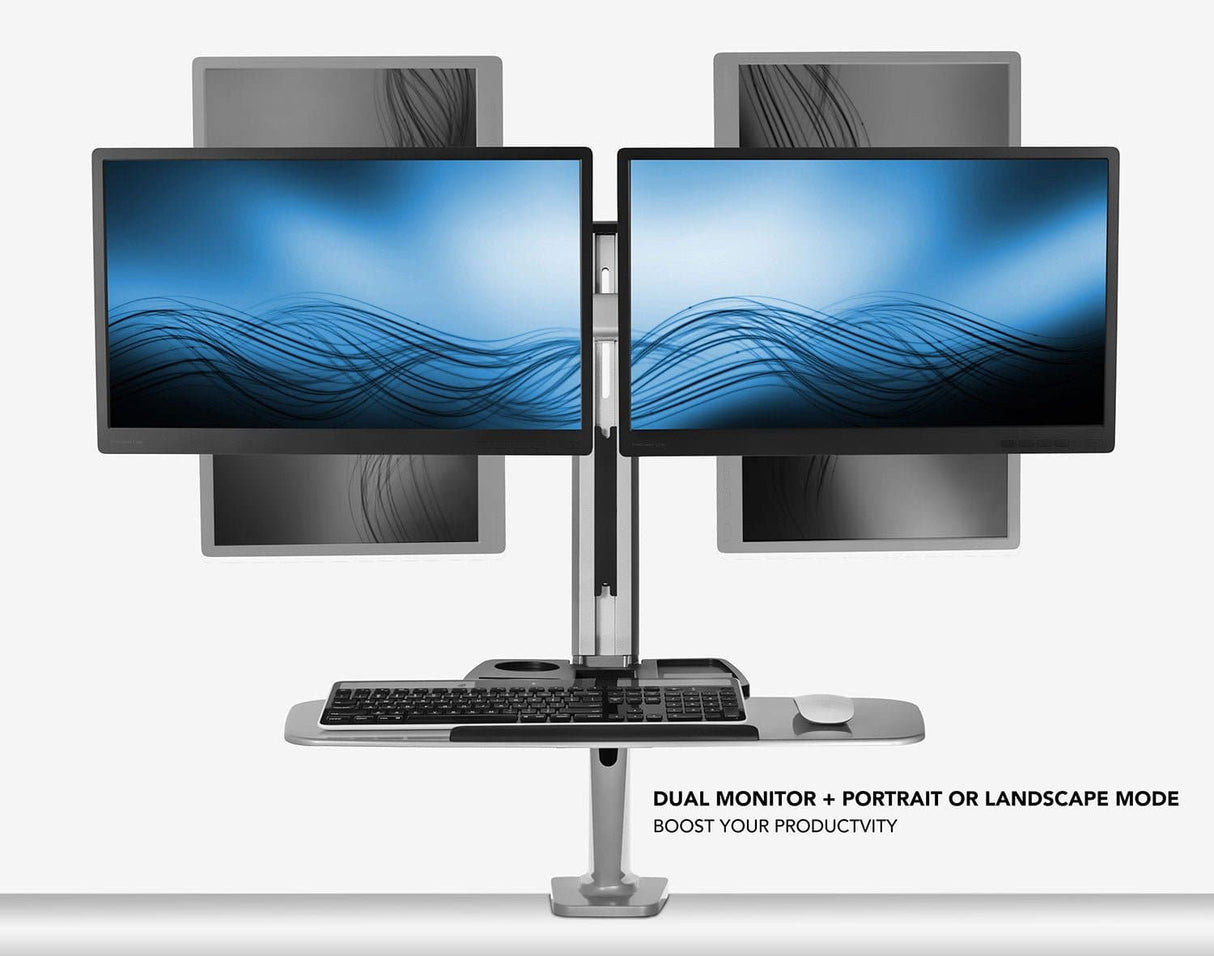
Dual Monitor Optimization
Dual monitors increase productivity by 25-50% when properly configured. Position your
primary monitor directly in front of your body, with the secondary monitor placed at a
slight angle (10-30 degrees) to reduce neck rotation. Both screens should be at the same
height to prevent vertical head movement.
For tasks requiring frequent monitor use, position monitors side-by-side with minimal
bezel gap. For reference work, place the secondary monitor at an angle that allows
easy viewing without forcing sustained neck rotation. Adjust brightness and contrast
to match between screens.

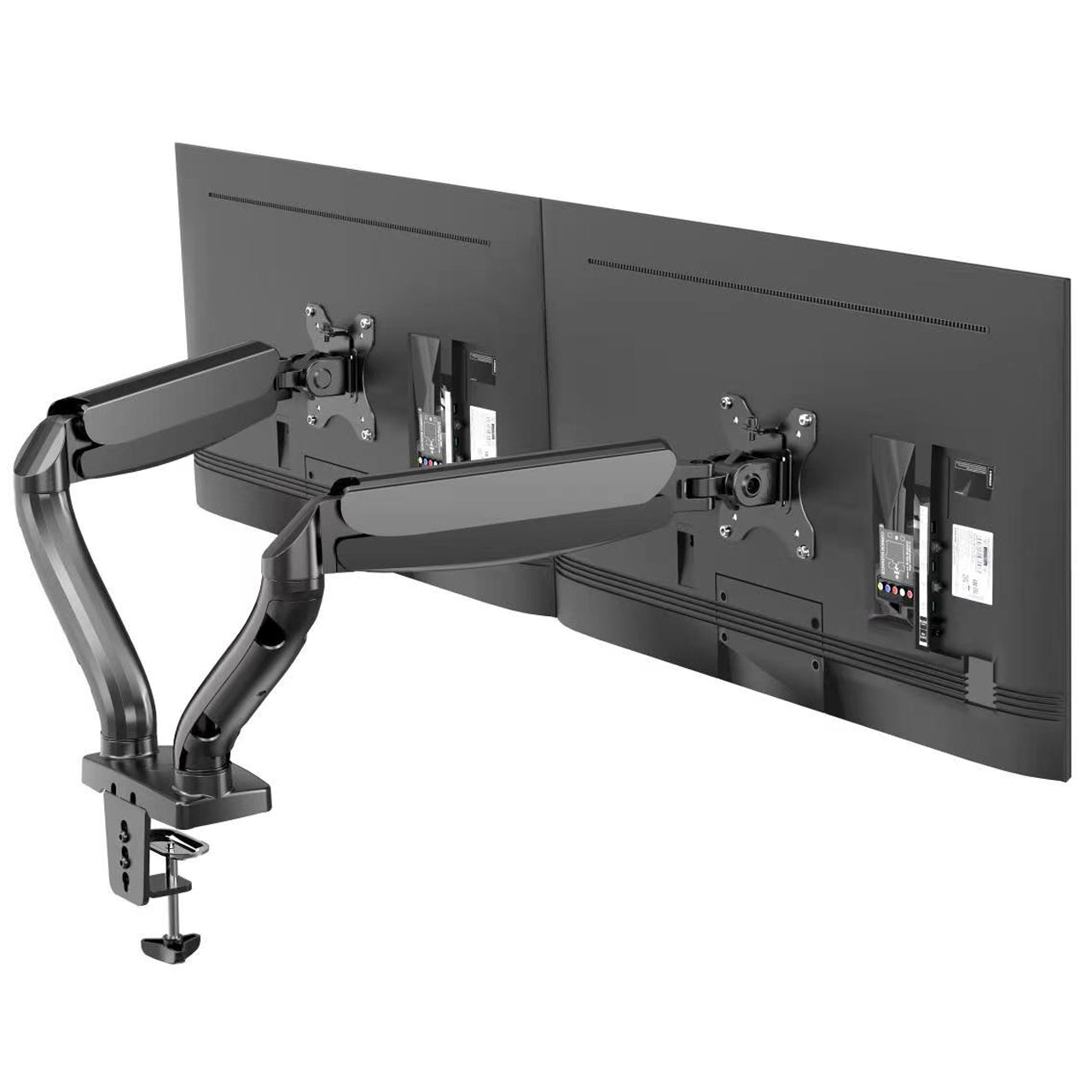
Beginner
Monitor Mount Types & Benefits
Monitor mounts free up desk space and provide precise positioning control. Desk clamp
mounts attach to the edge of your desk without drilling, while grommet mounts require
a hole but offer more stability. Wall mounts save maximum desk space but limit
repositioning flexibility.
Consider weight capacity, VESA compatibility (usually 75x75mm or 100x100mm), and
adjustment range. Quality mounts offer tilt, swivel, and height adjustments, plus
cable management features. The best mounts feel solid during adjustment and don't
sag under monitor weight.

Advanced
Triple Monitor Configurations
Triple monitor setups maximize screen real estate for complex workflows. Position
the primary monitor directly in front, with secondary monitors angled inward at 30-45
degrees. This creates an immersive visual field while minimizing neck rotation for
frequently-accessed content.
Use matching monitor models when possible to ensure color consistency and reduce eye
fatigue. Program hotkeys to move windows between monitors efficiently. Consider your
graphics card's capabilities - triple 4K displays require significant GPU power,
while 1440p monitors offer good performance with adequate screen space.

Quick Fix
Quick Monitor Height Check
Perform this 30-second check to verify optimal monitor positioning. Sit in your normal
working position and close one eye. The top of your primary monitor should align with
your open eye level, and you should be able to see the entire screen without moving
your head significantly.
If you need to raise or lower your chin to see the screen, adjust monitor height.
If you find yourself leaning forward to read text, either increase text size or move
the monitor closer. The goal is comfortable viewing without strain or excessive effort.

Beginner
VESA Mounting Standards
VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) mount patterns ensure compatibility
between monitors and mounting systems. Most monitors use 75x75mm or 100x100mm hole
patterns. Always verify your monitor's VESA pattern before purchasing mounts to avoid
compatibility issues.
Some larger monitors (32"+) may use 200x200mm or larger patterns. Weight capacity
ratings are crucial - under-rated mounts may sag or fail over time. Quality VESA
mounts include all necessary screws and spacers for different monitor thicknesses.
Advanced
Ultrawide Monitor Positioning
Ultrawide monitors (21:9 or 32:9 aspect ratios) provide immersive experiences and
eliminate the need for dual monitors in many cases. Position the center of the screen
directly in front of your body, ensuring you can see all content without excessive
head rotation.
Curved ultrawides work best when the curve wraps around your peripheral vision without
forcing you to move your head. For productivity, consider how software interfaces
work on ultrawide displays - some applications don't utilize the extra space effectively,
while others thrive with the additional screen real estate.

Quick Fix
Monitor Tilt & Angle Adjustment
Slight monitor tilt (10-20 degrees backward) reduces glare and creates more comfortable
viewing angles. Tilting the top of the screen slightly away from you helps maintain
proper visual focus while reducing neck extension that occurs with flat screen positioning.
Avoid tilting screens forward, which increases glare and forces uncomfortable head
positioning. Use tilt adjustments to compensate for desk height differences and ensure
the screen surface remains perpendicular to your primary line of sight for minimal
visual distortion.

Beginner
Screen Size & Resolution Planning
Larger screens don't always mean better ergonomics. Monitor size should match your
viewing distance and intended use. For standard desk setups (20-30 inches), 24-27"
monitors offer good balance between screen real estate and comfortable viewing.
Higher resolution (1440p or 4K) provides sharper text but requires scaling adjustments.
Consider your graphics card capabilities and typical viewing distance. 4K monitors
provide excellent clarity when positioned at proper distance, but may require scaling
to make text readable. Gaming or creative work benefits from higher refresh rates
and color accuracy specifications.








